Plagiarism involves taking credit for someone else’s ideas, words, or images, a practice considered unethical in academic and professional environments. It can go unnoticed by students who may accidentally rephrase someone else’s words without proper attribution. Since quotation marks are not used when something is paraphrased, it can easily escape the grasp of a proofreader and go on into the final draft. However, it is not entirely unachievable, especially since plagiarism checkers detect paraphrasing more efficiently nowadays.
Detecting paraphrasing can be a challenging task, as it involves identifying similarities and differences between texts. In the subsequent sections, we will delve into a comprehensive discussion about common methods and techniques employed to discern instances of paraphrasing.
How do plagiarism checkers detect paraphrasing: Suitable methods explored
In today’s educational landscape, plagiarism checkers have become increasingly advanced, going beyond only flagging copied text to also detecting paraphrased content. This article explores the methods allowing these tools to effectively identify paraphrasing.

1. String matching
This method involves comparing texts at the character or word level to pinpoint exact matches. A high degree of similarity in character sequences or word choices between two texts could signal paraphrasing. These tools employ complex algorithms that can even consider the contextual meaning of words, making it increasingly difficult for plagiarized, paraphrased material to go undetected.
2. Cosine similarity
Cosine similarity is one of the methods by which plagiarism checkers detect paraphrasing. It measures the similarity between two texts based on the angle between their vector representations in a high-dimensional space. By representing texts as vectors of word frequencies or embeddings, these tools can compute the cosine similarity score to further refine their ability to detect paraphrased content.
3. Word alignment models
These models align words or phrases between two texts to identify their correspondences. By comparing the aligned segments, you can detect paraphrasing based on similarities and differences in the matched sequences.
4. Semantic analysis
This approach involves analyzing the meaning and context of words and phrases in texts. Techniques like latent semantic analysis (LSA), word embeddings (such as Word2Vec or GloVe), or deep learning models like BERT can capture semantic relationships between words and identify paraphrasing based on the similarity of their semantic representations.
5. Machine learning
Supervised machine learning algorithms can be trained on labeled datasets of paraphrased and non-paraphrased pairs of texts. These models can learn patterns and features that distinguish paraphrases and can be used to classify new instances of text as paraphrased or not.
6. N-gram analysis
N-grams are groups of words that are right next to each other. When you check how often these groups appear in different texts and compare them, you can find similar phrases or sequences. If there are many similar patterns, it could mean that the text might have been paraphrased.
7. Near duplicate detection
The last way that plagiarism checkers detect paraphrasing effectively.
Near-duplicate detection algorithms are frequently employed in paraphrasing detection to pinpoint text segments that display a high degree of similarity or are almost identical. These algorithms are specifically crafted to recognize paraphrased content through the comparison of text similarity on a detailed level.
Which method is usually used by plagiarism prevention software?
Technological solutions utilized by professional plagiarism prevention services typically rely on n-gram analysis. By leveraging n-gram-based technology, these services achieve a remarkably high precision rate. This is one of the best ways plagiarism checkers detect paraphrasing, enabling the identification and highlighting of exact words that have been rewritten.
Mechanics of how plagiarism checkers detect paraphrasing
Plagiarism prevention services commonly employ the fingerprinting technique to compare documents. This involves extracting the necessary n-grams from the documents to be verified and comparing them with the n-grams of all documents in their databases.

Example
Let’s say there is a sentence: « Le mont Olympe est la plus haute montagne de Grèce. »
The n-grams (for instance 3-grams) of this sentence will be:
- Le mont Olympe
- mont Olympe est
- Olympe est la
- est la plus
- la plus haute
- plus haute montagne
- haute montagne de
- montagne de Grèce
Case 1. Replacement
If the word is replaced by the other word, still some of the n-grams match and it is possible to detect the word replacement by further analysis.
Changed sentence: « Le montagne Olympe est la plus haute montagne de Péloponnèse. »
| Original 3-grams | 3-grams of changed text |
| Le mont Olympe mont Olympe est Olympe est la est la plus la plus haute plus haute montagne haute montagne de montagne de Grèce | Le montagne Olympe montagne Olympe est Olympe est la est la plus la plus haute plus haute montagne haute montagne de Montagne de Péloponnèse |
Case 2. Changed the ordering of words (or sentences, paragraphs)
When the order of the sentence is changed, still some 3-grams match so it is possible to detect the change.
Changed sentence: « La plus haute montagne de Grèce est Le mont Olympe. »
| Original 3-grams | 3-grams of changed text |
| Le mont Olympe mont Olympe est Olympe est la est la plus la plus haute plus haute montagne haute montagne de montagne de Grèce | La plus haute plus haute montagne haute montagne de montagne de Grèce de Grèce est Grèce est Le est Le mont Le mont Olympe |
Case 3. Added new words
When the new words are added, there are still some 3-grams that match so it is possible to detect the change.
Changed sentence: « Le mont Olympe est de loin la plus haute montagne de Grèce. »
| Original 3-grams | 3-grams of changed text |
| Le mont Olympe mont Olympe est Olympe est la est la plus la plus haute plus haute montagne haute montagne de montagne de Grèce | Le mont Olympe mont Olympe est Olympe est de est de loin de loin la loin la plus la plus haute plus haute montagne haute montagne de montagne de Grèce |
Case 4. Deleted some words
When the word is removed, there are still some 3-grams that match so it is possible to detect the change.
Changed sentence: « L’Olympe est la plus haute montagne de Grèce. »
| Original 3-grams | 3-grams of changed text |
| Le mont Olympe mont Olympe est Olympe est la est la plus la plus haute plus haute montagne haute montagne de montagne de Grèce | L’Olympe est la est la plus la plus haute plus haute montagne haute montagne de montagne de Grèce |
Real-world example
Upon completion of verification in an actual document, paraphrased sections are often identified through interrupted markings. These interruptions, denoting changed words, are highlighted to enhance visibility and distinction.
Below, you will find an example of an actual document.
- The first excerpt comes from a file that has been verified using the OXSICO plagiarism prevention service:
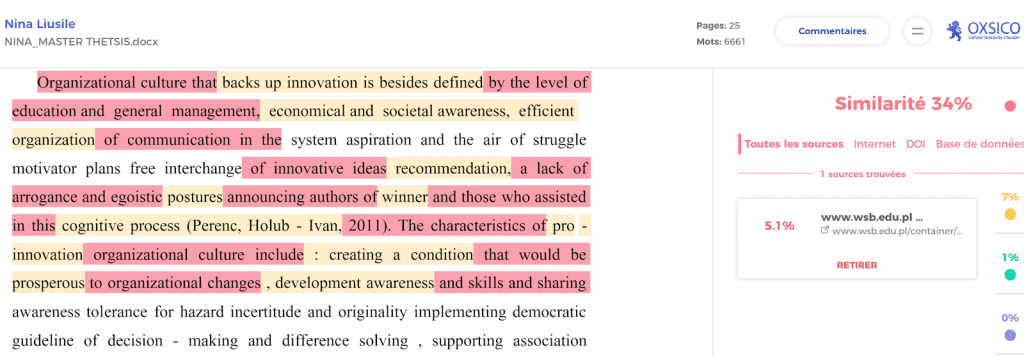
- The second excerpt is from the original source document:

After a deeper analysis it is evident that the selected part of the document was paraphrased by making the following changes:
| Original text | Paraphrased text | Changes |
| supports innovation is also characterized | backs up innovation is besides defined | Replacement |
| economic and social knowledge, efficient systems | economical and societal awareness, efficient organization | Replacement |
| proposals (ideas) | recommendation | Replacement, deletion |
| attitudes | postures | Replacement |
| success | winner | Replacement |
| process (Perenc, Holub-Ivan | cognitive process (Perenc, Holub – Ivan | Addition |
| pro-innovation | favorable | Replacement |
| creating a climate | : creating a condition | Replacement |
| favorable | prosperous | Replacement |
| developing knowledge | development awareness | Replacement |
Conclusion
| Plagiarism, frequently undetected in cases of paraphrasing, remains a significant concern in academia. Technological advances have equipped plagiarism checkers with the ability to effectively identify paraphrased content. Specifically, plagiarism checkers detect paraphrasing through various methods like string matching, cosine similarity, and n-gram analysis. Notably, n-gram analysis stands out for its high precision rate. These advancements substantially reduce the likelihood of plagiarized and paraphrased material going undetected, thereby enhancing academic integrity. |
